What is in the Road?
The Flexible Composite Construction has a Cement Bound Granular Material Base with an asphalt overlay. This solution offers a lower construction cost than a fully flexible pavement but provides the same quality.
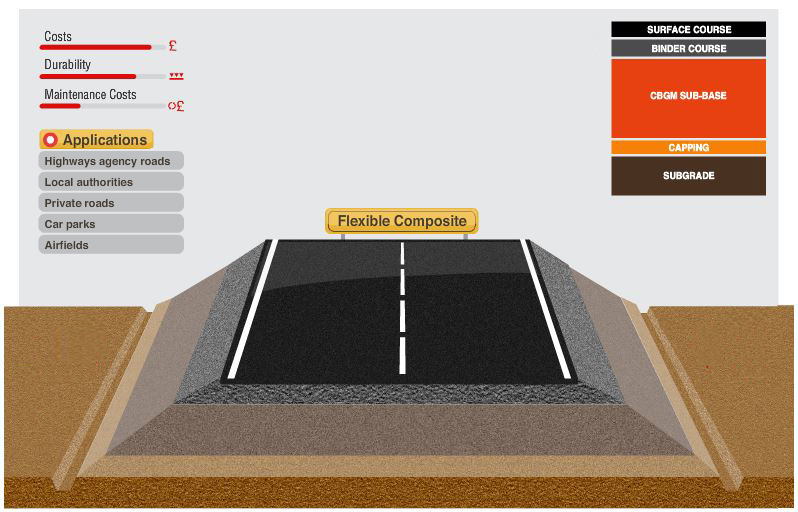
Surface Course
This is a mixture of bitumen-bound mineral aggregate carefully proportioned and mixed to the required specification. It can withstand the forces of traffic, transferring the loads to lower layers, and provides weather resistance, skid resistance and low traffic noise, among others.
Binder Course
This is the "lower part of the surfacing", and it is typically made of a type of asphalt concrete with different gradings of aggregates and types and quantities of binder depending on the particular needs of the road being built. This layer carries part of the load the surface has to deal with and also helps to waterproof lower layers.
Cement Bound Granular Material Sub-base
This is the lowest layer of the road construction, and is made of cement bound granular material containing crushed rock or gravel. This is the road foundation and it transfers the loads from above to lower layers, building up the strength of the road pavement.
Capping Course
This is a layer of granular product from crushed rock quarry, and often, recycled material. It provides a construction platform to work on if the subgrade is not strong enough on its own.
Subgrade Course
This is the existing ground, carefully shaped and compacted to the appropriate level and profile. Sometimes, if its strength is not enough to resist the expected loads, it can be improved by cement stabilisation.
The Rigid Composite Construction has a roller compacted concrete base with an asphalt overlay.
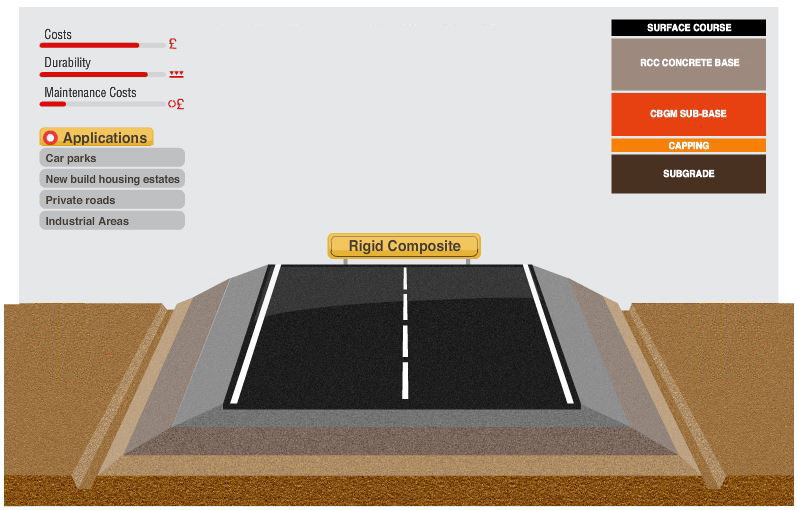
Surface Course
This is a mixture of bitumen-bound mineral aggregate carefully proportioned and mixed to the required specification. It can withstand the forces of traffic, transferring the loads to lower layers, and provides weather resistance, skid resistance and low traffic noise, among others.
Roller Compacted Concrete Base
Compacted in place and cured, this is a zero slump concrete that provides most of the properties of the asphalt concrete and it represents a competitive solution in terms of cost and durability when compared to asphalt.
Cement Bound Granular Material Sub-base
This is the lowest layer of the road construction, and is made of cement bound granular material containing crushed rock or gravel. This is the road foundation and it transfers the loads from above to lower layers, building up the strength of the road pavement.
Capping Course
This is a layer of granular product from crushed rock quarry, and often, recycled material. It provides a construction platform to work on if the subgrade is not strong enough on its own.
Subgrade Course
This is the existing ground, carefully shaped and compacted to the appropriate level and profile. Sometimes, if its strength is not enough to resist the expected loads, it can be improved by cement stabilisation.
The Rigid Construction has one thick layer of roller compacted concrete instead of any of the traditional asphalt layers. Often used in private infrastructure works.
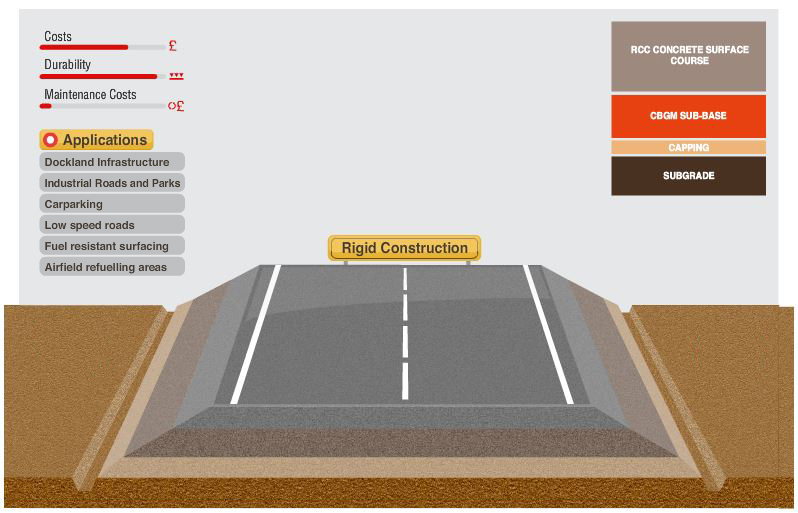
Roller Compacted Concrete Base
Compacted in place and cured, this is a zero slump concrete that provides most of the properties of the asphalt concrete and it represents a competitive solution in terms of cost and durability when compared to asphalt.
Cement Bound Granular Material Sub-base
This is the lowest layer of the road construction, and is made of cement bound granular material containing crushed rock or gravel. This is the road foundation and it transfers the loads from above to lower layers, building up the strength of the road pavement.
Capping Course
This is a layer of granular product from crushed rock quarry, and often, recycled material. It provides a construction platform to work on if the subgrade is not strong enough on its own.
Subgrade Course
This is the existing ground, carefully shaped and compacted to the appropriate level and profile. Sometimes, if its strength is not enough to resist the expected loads, it can be improved by cement stabilisation.
The Bituminous Flexible Construction is used in most of the roads around the UK and generally involves three layers of asphalt on a stone base.
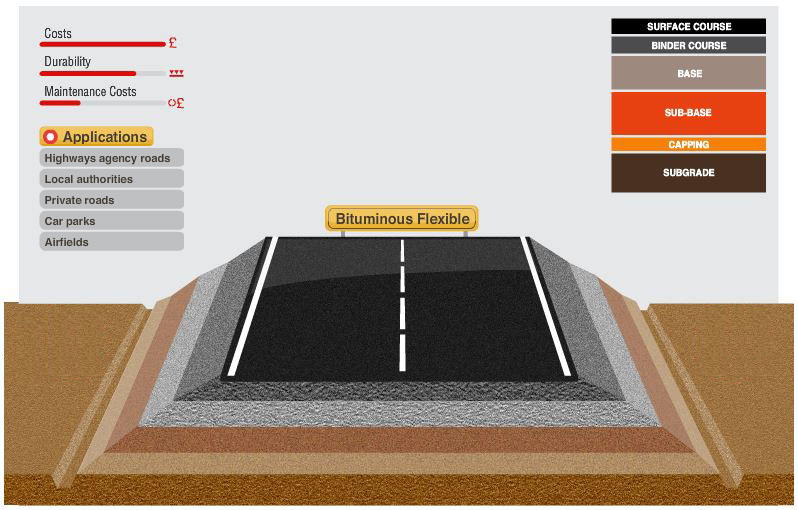
Surface Course
This is a mixture of bitumen-bound mineral aggregate carefully proportioned and mixed to the required specification. It can withstand the forces of traffic, transferring the loads to lower layers, and provides weather resistance, skid resistance and low traffic noise, among others.
Binder Course
This is the "lower part of the surfacing", and it is typically made of a type of asphalt concrete with different gradings of aggregates and types and quantities of binder depending on the particular needs of the road being built. This layer carries part of the load the surface has to deal with and also helps to waterproof lower layers.
Base Course
This is a type of asphalt that gets its strength and load-spreading capability from the interlocking aggregate skeleton (asphalt concrete). This is the principle structural layer that receives the loads from surfacing and provides most of the strength and load distributing properties of the road pavement.
Subbase Course
This is the lowest layer of the road construction, and is made of continuously graded crushed rock. This is the road building foundation and it transfers the loads from above to lower layers, building up the strength of the road pavement.
Capping Course
This is a layer of granular product from crushed rock quarry, and often, recycled material. It provides a construction platform to work on if the subgrade is not strong enough on its own.
Subgrade Course
This is the existing ground, carefully shaped and compacted to the appropriate level and profile. Sometimes, if its strength is not enough to resist the expected loads, it can be improved by cement stabilisation.